Fashion for the Earth
Toxic Textiles: The Chemicals in Our Clothing
November 4, 2022
Every week, the news labels a different consumable as “bad for you.” This trend can be seen in our food, medicine, and drinking water. All of which have been described as riddled with carcinogens, hormone disruptors, forever chemicals, and toxins. Unsurprisingly, all these harmful chemicals can be found within our wardrobes and throughout the textile industry. More importantly, the health implications of these substances are vast in range, and volume, as approximately 25% of global chemical output originates from the textile industry. Since textiles comprise a significant part of our world, and we are in contact with textiles all day, every day, safety and confidence in these products are vital.
Good versus Bad
There is much talk about what is good or bad for you, so before we dive into the specific chemicals in our clothing, it is essential to note that Chemicals are not inherently bad. All matter is made of chemicals! That includes you and me. While it is true that not all chemicals are “good” for us—and even those that are, namely water, can be harmful when exposed to too much of it—the word chemical should not be feared.
What are these “bad” chemicals?
There are about 8000 synthetic chemicals that are used in the apparel industry manufacturing process, from material acquisition to the finished product. Since we cannot cover every chemical and its function, this article will focus on the most common and deleterious substances. These include, but are not limited to, flame retardants, Polyfluorinated substances (PFAS)*, lead & chromium, phthalates, chlorine bleach, AZO dyes, and volatile organic chemicals (VOCs)+ such as formaldehyde. Please see the infographic below for a more in-depth look at chemicals and associated health concerns. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive list.
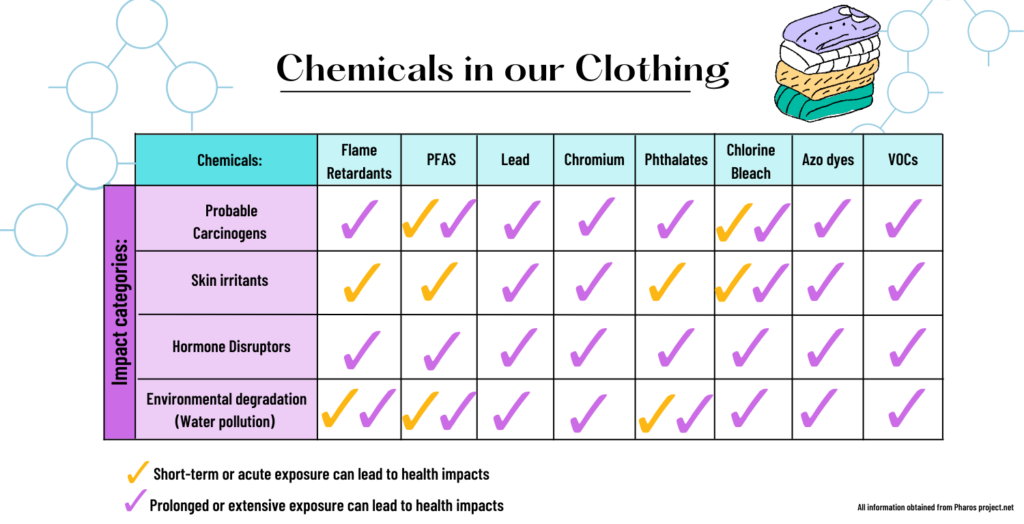
Function matters, but at what cost?
These chemicals were not created to be “bad,” but does their intended purpose eclipse their adverse effect? Let’s take a look
- Flame retardants were designed to stop clothing from burning and are required for children’s clothing. This helpful technology has been linked to bioaccumulate (the chemical/material builds up in the bloodstream) health risks, including infertility, neurotoxicity, endocrine disruption, and cancer.
- PFAS materials are fluoropolymer coatings/products that are popular due to their ability to resist water, oil, heat, and stains. You can often find these materials in raincoats, shoes, cosmetics, mattress pads, printed natural and synthetic fabrics, and finished textiles labeled as water or stain-repellents. However, these chemicals have also found their way out of their intended products into our environment, drinking water, and food. Thus, they are known to bioaccumulate and are often recognized as environmentally persistent and carcinogenic.
- Lead & Chromium (VI) are heavy metals that come in different forms. They can be found in rocks, plants, animals, and soil. Lead is a heavy metal found in natural fibers such as cotton, hemp, and flax. In the manufacturing process, Lead and Chromium (VI) materials are used to stabilize the color in the dyeing process. You can find these elements in vividly colored synthetic products. While these are naturally occurring, when high concentrations of these chemicals come into contact with the skin, are absorbed, or ingested, they have been linked to cancer and contact dermatitis. Additionally, when clothing containing these compounds is washed, during both the manufacturing process and later by consumers, they can cause environmental damage.
- Phthalates are used in activewear and anti-odor clothing, printing inks, and processing. Phthalates are a plasticizer, used with rubber to print images onto garments, and are predominately known to be cancerous. They have also been linked to endocrine disruption.
- Chlorine bleach, a whitening and stain removal agent, can cause severe asthma and respiratory problems. It is often used to process natural fibers such as cotton (think denim) and to prepare polyester for dyeing. Chlorine bleach and solvents such as chlorobenzenes can be toxic by inhalation or skin contact.
- AZO dyes make up 60-70% of fabric colorants and are responsible for the vivid colors that can be seen in many textiles, especially clothing concentrated in black and brown pigmentation. Azo dyes can quickly come off fabrics and, once in contact with the skin, break down to release chemicals called aromatic amines, causing skin allergies and dermatitis, some of which have been reported to cause cancer.
- Solvents, adhesives, plastic & metal accessories, synthetic dyes, and fibers used during the production process release VOCs. Some common VOCs are formaldehyde, toluene, ethylene glycol, benzene, methylene chloride, 1,3-butadiene, xylene, and tetrachloroethylene. These chemicals allow for an easy-care finish, such as wrinkle-free products. However, VOCs are a huge occupational hazard, as off-gassing can cause developmental and reproductive system damage, skin/eye irritation, and liver and respiratory problems.
How can I stay safe?
When looking at your wardrobe, seek materials, fabrics, and dyes that are considered natural (cotton, wool, silk, leather) rather than synthetic materials. Check for third-party certification standards such as the Oeko-Tex Standard 100, Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), the EU Ecolabel, or the bluesign® certification.
Fashion for the Earth is EARTHDAY.ORG’s mission to educate consumers and provide them with enough information to be safe and sustainable and ultimately challenge the industry for the better.
